|
Overview: India is one among the countries rich in water resources in the world. According to Central Water Commission’s annual report 2014-15 rainfall in India varies from 100 mm in Western most regions to 11000 mm in Eastern most region. The estimated average annual rainfall in India is 117cms. Central water commission estimates that the average annual precipitation is 13200 TMCft (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) in which about 9900 TMCft of water precipitates during monsoon. The overall natural runoff and estimated utilizable surface water resources is 6555.45 TMCft and 1980 TMCft respectively. Along with this about 1320 TMCft ground water is also available for utilization. As per Central Water Commission (CWC) which makes periodic assessment of the country‘s water resources estimates water resources potential of the country that naturally runoff in the rivers is about 6167.7 TMCft. But due to various constraints of topography and uneven distribution over space and time, only about 3705 TMCft of the total annual water potential can be put to beneficial use. This can be achieved through 2277 TMCft of utilizable surface water and 1428.9 TMCft through ground water. While water for drinking purpose has been accorded top most priority in water use, irrigation is the major consumer of water. Ultimate Irrigation Potential which can be created through major and medium irrigation projects is assessed as 58.47 Mha. Besides this, an additional irrigation potential about 35 Mha can be created by taking up long distance inter basin transfer of water from surplus to deficit basins. Though India has enough water resources, majority of the Indian states are facing severe shortage of water in every summer for both drinking and agriculture purposes. Currently water crisis especially for drinking purpose prevails everywhere. Agriculture – The backbone of Indian economy and its supportive activities such as animal husbandry, sheep and goat rearing are severely affected. The people depending on agriculture for their livelihood are struggling to lead their lives due to huge shortage of water for agriculture activities.
Both natural and manmade disasters are contributing for the current situation. Unequal distribution of rainfall and its space, time, duration on one hand and poor water management, conservation, utilization, due to lack of water literacy, awareness, concern commitment are another hand. The illegal sand mining, deforestation, threat from plantation of eucalyptus and acacia, over exploitation of underground water for agriculture use, encroachment of forest lands, lakes and rivers are also playing vital role in decreasing the rain fall as well as depletion of ground water. Crop patterns also one among the major reasons for over exploitation of ground water in different parts of the country. Manmade disasters are contributing more for this water crisis than natural disasters. Hence, it is the time for spread awareness and manages the water resources fruitfully for the current and upcoming generation too. Problem Statement: India has much diversified agro climatic zones with varied rainfall in space, time and intensity. Country receives an average rainfall of 268 cm in the total geographical area of 19% and yields 56% of the total water resource that is nearly 36,228 TMC. About 46% of the total geographical area receives 121 cm yields 24,471 TMC of water which is 37% of the total water resource of the country. And remaining 35% geographical area receives just 65 cms of rain yields only 4,819 TMC of water which is just 7% of the total water resource of the country. Central plains of Tamilnadu, Karnataka, Maharastra, Gujarath and Rajasthan falls under this 35% of water stress geographic area where more than 30% of the total population of the country and live stock lives in. Indeed silk, milk, vegetables, flowers, fruits and majority of agriculture products producing and transporting to other parts of the country from this area. Currently due to unscientific use of available water, lack of water literacy and management skills, the agricultural activities are severely affected and farmers are moving towards urban and semi-urban areas. Districts namely Chickaballapura, Kolara, Tumkuru, Bengaluru Rural, Ramanagara and Chitradurga have facing severe water problem for all purposes despite the statistics from Indian Metrological Department shows there is no deficit rain fall in Interior Karnataka since 2004 except 2012. The situation of farmers in the said districts is literally pathetic as ground water level has gone to 1,500 feet from 200- 300 feet, all rivers flowing in this region are dried up, lakes are became spots of illegal sand mining as no water stored due to excess of silt, some parts of lake beds along with main and sub cannels are encroached by neighbor farmers which makes the rain water to stagnant in the same place rather than flowing into the lakes. As a result there is no or less water stored in lakes and tanks through which ground water recharge is not possible. The illegal sand mining in lake beds and growing eucalyptus are major threat to ground water in the said districts of Karnataka. If the situation continues like this, said districts will become desserts. In order to prevent from this alarming situation, it is necessary to study and manage the available water for the current needs and for the future too, which could be done through scientific and visionary water budgeting. Water Budget: Water budget is the method of scientific understanding, studying, calculating and managing the available water resources. It also explains the optimum utilization of available both surplus and ground water to meet the needs of human being. Through water budget, it is easy to understand the rain patterns, rainfall duration, intensity, topography, land use, situation of water bodies, storage capacity of water bodies, water flow cannels, crop pattern, soil kinds and issues affecting to water crisis and so on. It also acts as a plan for harvest and optimum utilization of rain water for drinking as well as agriculture purposes. Aim and Objectives: The main aim of framing water budget is to study, understand, calculate and manage the available water resources scientifically and bring out a concrete plan of action for optimum utilization of both surplus and ground water. In order to meet the aim, the following objectives are delineated.
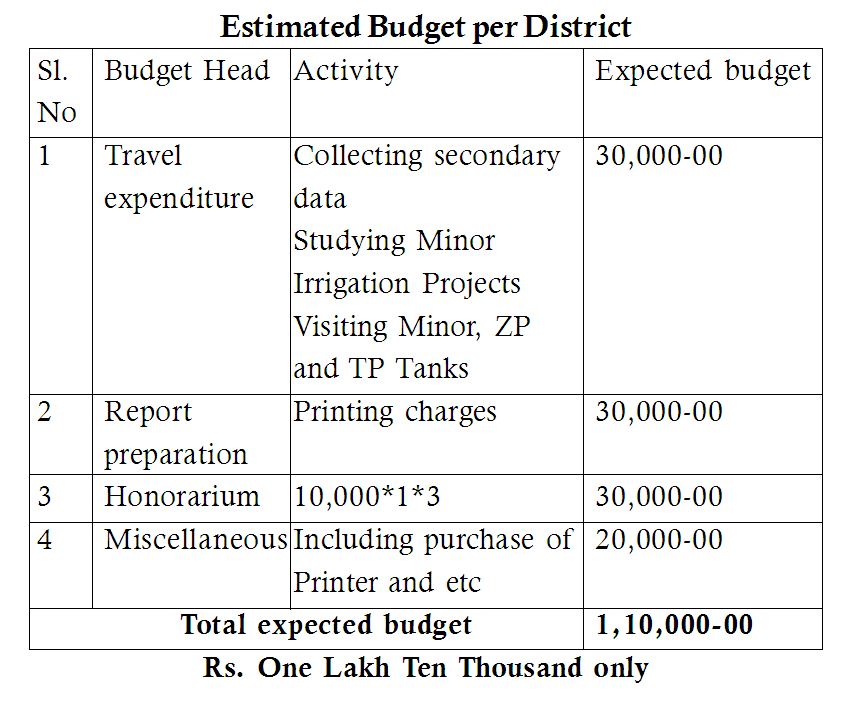
Initially, the focus is on undivided Kolara (Kolar and Chikkaballapura districts) district known as vegetable basket, fruit bowl, Flower Bouquet, Milk can & Silk bag for the entire Karnataka state. Once it was green and prosperous district by maximum utilization of 4289 irrigation tanks, surface water, around 60,000 open wells and ground water. But the situation has been changed now and people are facing severe water crisis even for drinking purpose. Studies have shown the said districts would become desserts soon if the situation continues. Undivided Chikkaballapur and Kolar districts are situated in southern plains of Karnataka state. They are at equidistance of 300 kms from both western Arabian and eastern bay of Bengal on contrary. Western and Eastern ghats are situated in both the sides of the districts which blocks the south west Monsoon and North east Monsoon clouds. Hence these Districts fall in the rain shadow area and get an average annual rain fall of just 680 mm. There are droughts and famines which are very common and frequent guests of Chikkaballapur and Kolar dstricts. People due to this will experience socio-economic and ecological imbalances. The districts are situated at an altitude of 700-900 meter mean sea level having more than 2,893 villages, where there are more than 32 Lakhs human population and probably these are the densely populated districts in Karnataka state. There are three rare and distinct river valleys namely North Pinakini & South Pinakini & Palar basins and its small tributaries jayamangali, Kumadvathi, Pinakini, Kushavathi, Chitravathi, Vandaman, Papagni, Palar, Koundinya, Markandeya, South Pinakini etc, in the said districts. The districts spread with an area of nearly 7,951sq km having more than 4,289 irrigation tanks including Taluk Panchayat, Zilla Panchayat, Minor irrigation tanks of different sizes and capacity. The total water spread area of all tanks/lakes is approximately 46,174 hectare with water holding capacity of nearly 39 TMC of surface water and irrigating nearly 70,748 hectare of tank/lake acchukattu. The water storage depth of water in lake/tank beds is just 2.39 meters in which potential evaporation and infiltration lose approximately 1.2 meter and 1 meter respectively. Finally, about half meter of water will be available for farmers’ utilization. Hence, almost all tanks are becoming un-useful as they are filled with silt and they need to be rejuvenated in scientific manner. Scope: Water budget is the concept that focuses on the study, understand, calculate and manage the available water resources in scientific manner and bringing out a concrete plan of action for optimum utilization of both surplus and ground water. Water budget focuses on rejuvenating traditional water bodies like irrigation tanks, lakes, rivers for better water conservation and utilization at micro level and interlinking of rivers and diversion of inter basin water projects for irrigation projects at macro level. It gives a clear cut picture of available water and its sources, rainfall patterns, situation of lakes and tanks in each village and its spread area, means of water storage and ground water recharge, Optimum utilization of rain water and it’s harvesting for various purposes etc. Hence this model will be useful for each and every person in the society. For governments which are dealing with the water issues, the water budget shows a path to curb the water problems. Indeed, the water budget may helpful to farmers to change their crop patterns according to water availability and kind of soil. A study to prepare water budget will conduct by Usirigaagi Hasiru in collaboration with Mr. Chowdappa D. A. well-known environmentalist. Initially the present study focuses on Chickaballapur district and later we have plans to focus on other districts of Bayaluseeme based on availability of funds. The study process will starts in the month of May 2017 and completed by July 2017. The estimated budget for conducting the present study is given below. Usirigaagi Hasiru – A group of five likeminded youth having deep concern towards environment protection initiated with the aim of protecting environment and creating awareness among common public especially the youth and the children. Initially the focus was on protecting environment by planting various kinds of saplings at public places and motivating the community to take up the responsibility of protecting them by watering. In order to ensure the growth of the planted saplings, the members have initiated follow-up visits on fortnightly basis and have contact with the community constantly. Since the inception of the group, plantation programs have been taken place in the premises of schools, colleges, community halls, primary health centers, Lake beds, Gomala and Grazing fields. At this juncture the members have also continuously been involved in taking care of the saplings in the community where there are more than 100 saplings being planted. Apart from the plantation drives, the members have also initiated seedlings, creating awareness on discouraging the use of plastic, Silent March- Demanding for eucalyptus free forests and Research on adverse effects of eucalyptus on agriculture and ground water. Usirigaagi Hasiru started on 26.01.2015 with no legal entity, has successfully completed two years of its existence by winning the confidence and unconditional support of the community the group has also been recognized for the prestigious Yuva-Chetana Award sponsored by Youth for Seva Organization for its dedication and commitment for promoting healthy and green environment. The group has gained its legal status through registering under the Trust act on 17.12.2016. |
Categories
All
Social Work Learning Academy50,000 HR PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS. MHR LEARNING ACADEMYGet it on Google Play store
|
SITE MAP
SiteTRAININGJOB |
HR SERVICESOTHER SERVICESnIRATHANKA CITIZENS CONNECT |
NIRATHANKAPOSHOUR OTHER WEBSITESSubscribe |
MHR LEARNING ACADEMY
50,000 HR AND SOCIAL WORK PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
|
|








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





