|
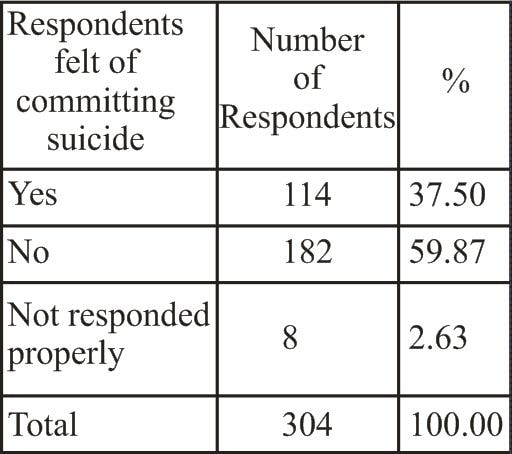
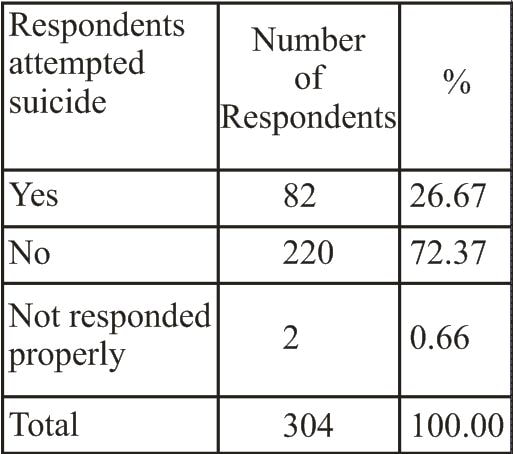
Abstract Just as heterosexuality is considered as a norm in the society homosexual relations and homosexuality are looked as repulsive and abnormal. Sexual minority as a community is marginalized, excluded and deprived from the wider links to main stream community life due to their sexuality. Stigmatization around feminization produces a range of problems from verbal abuses to threats to their life. Stigma, denial and violence push them to severe health problems especially mental health problems. From their childhood to old age they undergo lots of crisis. They are forced to go away from their family at younger age. It is difficult to live in a stigmatized society without family support. This produces enormous psychological consequences such as stress, depression, anxiety, loneliness, self-destructive behavior. Suicidal tendency is very common among sexuality minority. Majority of them have attempted for suicide at least once in their lifetime. Since our society is more homophobic and homosexuality is considered as abnormal, these mental health issues are ignored. This article attempts to understand the problem of suicide among the homosexuals. KEY WORDS: sexuality, homosexual, homophobia, mental health, violence, stress Introduction Just as heterosexuality is considered as a norm in the society, homosexual relations and homosexuality are looked as repulsive and abnormal. Sexual minority as a community is marginalized, excluded and deprived from the wider links to main stream community life due to their sexuality. Though the sexual orientation is between the two same sexes biologically, sexual relations and actions are constructed in such a way in which if one individual is feminine in his orientation and another as masculine. A male being a feminine in his actions and attitudes in general and particular in relation sexual attitudes and actions is considered as aberrant from widely held norms, beliefs and values of the rest of society. Male homosexuals, hence, attract the wrath of others who vary from elders and parents in family, friends and to neighbours in primary group relations to wider social networks. Stigmatization around feminization produces a range of problems from verbal abuses to threats to their life. Stigma, denial and violence push them to severe health problems especially mental health problems. From their childhood to old age they undergo lots of crisis. They are forced to go away from their family in younger age. It is difficult to live in a stigmatized society without family support. This produces enormous psychological consequences such as stress, depression, anxiety, loneliness, self destructive behavior, etc. Suicidal tendency is very common among sexuality minority. Majority of them have attempted suicide at least once in their lifetime. Since our society is more homophobic towards individuals who deviate from societal sexual norms and beliefs, which is heterosexual, homosexuality and homosexuals are considered as abnormal. Mental health problems of male homosexuals, therefore, emanating from denial of their identity are hardly recognized and cared. The WHO removed homosexuality from its list of mental illnesses in 1981(www.who.org).The American Psychiatric Association removed homosexuality from its list of mental illnesses in 1973, though keeping ego-dystonic homosexuality within the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). In 1986, even this was also removed (http://www.psych.org/ public_info/ homose~1.cfm). The American Psychological Association similarly removed homosexuality from its list of disorders in 1975. (http://www.apa.org/pi/lgbc/ guideline.html#top,http://apa.org/pi/statemen. html) Till July 2009 homosexuality was considered as a crime in India. In July 2009 this act has been amended. The High Court of Delhi ruled that the provision in Section 377 of India's Penal Code that criminalizes private consensual sex between same-sex adults violates the country's Constitution and international human rights convention(ibid, italics are added). Homosexuals are stigmatized and discriminated in the society. Due to the stigma, internalized homophobia, discrimination, lack of family support makes them undergo plethora of psychological problems. The heterosexual norms in the society and homophobia forbid them from expressing their sexuality. But it is very difficult for them to fit into the usual heterosexual norms. It makes their condition more perplexed. Every child gets its basic psychological needs like love, care, affection, support, protection from its parents and family. But sexual minorities' are deprived from them; instead they undergo humiliation, scolding, mental torture, physical violence, ignorance, intolerance, negligence, etc. Such experiences are not confined merely to the sphere of family, but also encompass the circles of friends, classmates, neighbours, relatives, teachers, etc. Femininity makes them more vulnerable. Due to their femininity they often undergo humiliation, physical torture, sexual abuse, kidnap, rape, other sexual violence, blackmail etc. When they are forced to have entered into married life, they have lots of problems and pain to experience. Usually many homosexuals don’t show any sexual interest in opposite sex. Our values prescribe that life of an individual is completed only when he/she is married. Parents and family members, therefore, put an enormous pressure to get married. Several suicide cases were reported when homosexuals were pressurized to marry. Present article is a study based on primary data conducted in the Dharwad district of Karnataka with an intention to understand the suicidal tendency and suicidal attempt among the male homosexual community. This study intends to examine the macro situation discussed above in micro context as different studies show that homosexual people suffer more and severe psychological problems compared to the others. Methodology: Subjects of the present study are Male homosexuals. Respondents were approached in drop in centers (DIC) of the NGOs, both in Hubli and Dharwad. Respondents across Dharwad district, Dharwad, Hubli, Navalgund, kundogola, Annigere, Alnavara and kalaghatagi Towns, visit the DICs. Two set of data collection techniques were administered for collecting data: a) Interview schedules and b) Focus group discussion. The sample size of our study is 304. Type of sampling adopted to select the respondents for the study was ‘convenience sampling’. Following are the major issues we have come across in our study which are presented below. Suicidal tendency and suicidal attempt among the homosexuals Recent North American and New Zealand studies of large populations reveal that young LGBT(Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender) people can have rates of suicide attempts at least four times those of their heterosexual counterparts (Elizabeth McDermott, Katrina Roen & Jonathan Scourfield,2008). Emile Durkheim, an eminent classical sociologist, identified four distinct patterns of suicide. The three patterns most commonly referred to are ‘egoistic’ suicide, ‘altruistic’ suicide and ‘anomic ‘suicide. Egoistic suicide is committed by people who are not strongly supported by membership in a cohesive social group. As outsiders, they depend more on themselves than on group goals and rules of conduct to sustain them in their lives. In times of stress, they feel isolated and helpless. Altruistic suicide is committed by people who are deeply committed to group norms and goals and who see their own lives as unimportant. Basically, these suicides involved dying for a cause. Anomic suicide is committed by people when society is in crisis or rapid change. In such times, customary norms may weaken or break down. With no clear standards of behavior to guide them, many people become confused, their usual goals lose meaning, and life seems aimless. (cuip.uchicago.edu/~lderbach/msw/xsdurkhm.pdf) Taking decision to end one’s life reflects the state of acute distress a person has been undergoing. Situations of suicides which are already committed, thwarted attempts and a thinking to commit suicide are apparent revelation of lack of vibrant and strong social structure. Reasons expressed for suicide cases and failed attempts of homosexuals indicate or point towards ‘internalized homophobia’, loss of loving relationships, break down of love affair, social phobia, adjustment problems with family and relatives, black mail, etc. Couple of both enfeebled social structure-lack of integrating and supportive social relations-and void in social norms account for the above reasons expressed by respondents. Lack of adjustment with family members and relatives is a pointer at lack of integrative relationship with group life. ‘Anomie’-a state of absence of norms appropriate for social interaction in situations. Norms regulate the actions of individuals and provide proper orientation to situation. Anomie refers to break down of these norms caused by sudden and unexpected changes which again are caused in some times by major catastrophes such as wars, revolt, loss of loving relationship and love affair etc. The following table shows the rate of suicidal tendency among the homosexuals. Table 1 Suicidal Tendency Table 1 provides information about suicidal tendency of homosexuals that is suicidal feelings. Around 37 per cent of respondents (n=114) have felt of committing suicides. Around 60 per cent have expressed that they have not undergone such feelings. Around 3 per cent of the respondents have not responded properly. Table 2 Suicidal Attempt
Table 2 is concerned with suicide attempts of homosexuals. Table 2 shows that 27 per cent of the respondents have attempted suicide at least once in their life. According to National Crime Records Bureau, the suicide rate of the general population is 9.6 in one lakh (0.0096%) in Karnataka in the year 2009(Annual report of National Crime Records Bureau 2009). Studies say that suicide attempters are ten times the suicide completers. If we apply the above criterion then we can safely juxtapose that Suicide completers among the homosexuals may, therefore, be 2.69%. Suicide rate, then, among our respondents is 280 times higher than the suicide rate prevailing among general population. This shows the gravity of the problem that homosexuals are undergoing. Following are the reasons we come across for their attempted suicide. 1. Due to internalized homophobia homosexuals often feel guilt, disgusted about themselves and fear about their sexual identity being disclosed to their family. 2. Once their identity is disclosed to their family, parents and elder brothers usually start giving physical and verbal torture. They are excluded from decision making process of the family matters. They are humiliated often. They are pressurized to get married which makes them to give up the relations or to leave the home altogether. This alienation of homosexuals from their primary relations makes them enfeebled. 3. Loss and or break of relationship with their partners is a fatal blow to already aggrieved due to alienation from familial and neighbourhood relations. They, then, undergo the feelings of committing suicide. It is difficult for them to tolerate. 4.BhilaPanthis2 often black mail them on disclosing their sexual relations with the family and in work place. 5. Once their identity is disclosed people in the surroundings especially neighbours and relatives humiliate them giving verbal and physical torture. This pressurize them to leave their family. Conclusion Mental health is a core aspect of human life. Without sound mental health one cannot enjoy his/her life and cannot have control over their life. Ramifications of lack of sound mental health are not only confined to individual life sphere but also have significant consequences on development process of any nation. The person who does not possess a good mental health can not participate effectively in social, economic and political processes of the country. People who are not mentally well are excluded from the mainstream of society and the result is apparent, that is, marginalization and social exclusion from wider network of society. Homosexuals who are marginalized are, hence, easy prey to domination and oppression. Homosexual’s problems are rooted in our social structure- social norms, traditional gender values. Denial from the family, society, internalized homophobia, humiliation from the people around them, confusions about gender roles and one’s own sexual identity make them more vulnerable to mental health. This study reveals alarming outcomes. 38 per cent of the respondents underwent the suicidal tendency and this is not a negligible number. The ratio is more than 3:1. 27 per cent of them already attempted suicide. This is almost one in four attempted suicides which show the severity of the issue. But unfortunately the state and civil society have least interest in the issue and even other organizations which work for the homosexuals also mainly focus on HIV/AIDS and have shown little attention to mental health issues. There is an urgent need to focus on this issue as homosexuals, as a community, have been suffering from mental health problems which curb the personality of the individuals and at the same time deprive them from effective participation in socio-economic development of our country. Reference: 1. A report of national crime records bureau ,Ministry of home affairs, 2009, http://ncrb.nic.in/CD-ADSI2009/ADSI2009-full-report.pdf 2. A report of PUCL-Karnataka February 2001 3. Chakraborty, A. ,Mental health of the non-heterosexual population of England. British Journal of Psychiatry, Vol. 198, February 2011, pp. 143-48. 4. Decriminalizing Homosexuality in India, Geethanjali Misra, 2009, http://www.countmeinconference.org/downloads/RHM.MISRA.pdf 5. Joseph Sherry, 2005 “Social work practice Men Who Have Sex with Men”, New Delhi, Sage publications 6. Ken Morrison,2008 “Marx Durkheim Weber; formations of modern social thought”, New Delhi, Sage publications 7. Ram Ahuja, 2003 “Research Methods”, jaipur, Rawat Publications 8. www.who.org. Note 1. Drop in centres are the resting places for the community. 2. Panthi is a homo sexual identity, act dominant role in sexual activity. BhilaPanthi is one who had sex with them and after which give trouble by physical torture, black mail etc., Supriya P R. #1708, Raghavendra Nilaya, Behind Alahabad bank, Gandhi nagar, 2nd cross, Mandya, Karnataka Mob:9480369666 Dr.C. Usha Rao Reader, Department of Studies in Social work, Manasa Gangothri, Mysore University, Mysore-06, Karnataka |
Categories
All
Social Work Learning Academy50,000 HR PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS. MHR LEARNING ACADEMYGet it on Google Play store
|
SITE MAP
SiteTRAININGJOB |
HR SERVICESOTHER SERVICESnIRATHANKA CITIZENS CONNECT |
NIRATHANKAPOSHOUR OTHER WEBSITESSubscribe |
MHR LEARNING ACADEMY
50,000 HR AND SOCIAL WORK PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
|
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





