|
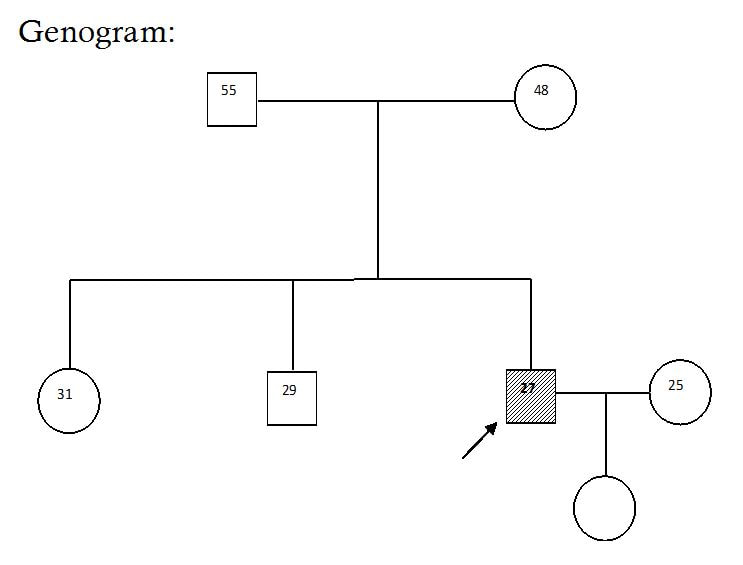
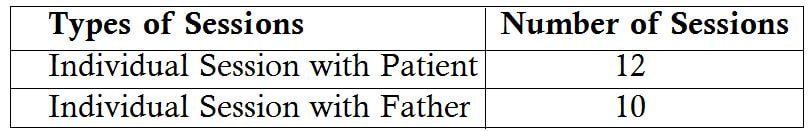
Abstract Bipolar Affective Disorder (BPAD) is a psychological illness that involves severe mood swings. These mood swings take the form of depression or mania and may last for several months at a time. Depression which effects both the mind and the body and it is a leading cause of disability, workplace absenteeism, decreased productivity and high suicide rates (Michaud, et al 2001). During mania patients often have increased libido, need less sleep, have excessive energy and can sometimes engage in risky behaviour (such as gambling excessively) or can even become violent. In this regard an effort has made to explain the management of a case which is diagnosed as Bipolar Affective Disorder currently Mania with Psychotic Symptoms, detailed psychosocial assessment explored significant factors wherein he was not able to cope up with the same. Multidisciplinary team work helped him to reach a better functional level. Keywords: Bipolar Affective Disorder, Mania, Depression, Psychotic Symptoms Introduction Bipolar affective disorder (BPAD) is an episodic illness in which episodes of depression/Mania/Mixed/Hypomania occur. BPADs are dimensional illnesses in which patients’ experience, long-term course of illness, fluctuating levels of severity of manic and depressive symptom interspersed with symptom-free (euthymic) periods.(Judd et al. 2005) Patients with BPAD encounter educational difficulties, job related problems, interpersonal difficulties, psychosocial dysfunction, disability, marital problems, multiple suicidal attempts, completed suicide and medication side effects. Additionally patients with BPAD have high rates of physical and psychiatric comorbidity. The prevalence rates of BPAD vary from country to country. The age group between 40 and 49 years was predominantly affected (psychotic disorders, bipolar affective disorders (BPADs), depressive disorders, neurotic and stress-related disorders. (Murthy 2017) Hence in this connection the current article has briefed a case of a patient with Bipolar Affective Disorder currently Mania with Psychotic Symptoms who had significant psychosocial stressors. Socio-demographic details: Mr. H is a 27 years old male studied up to 9th standard, working in a FMCG factory in packing department from middle socio economic status from Nelamangala, Karnataka. Reasons for referral: To assess the patient’s disability level for work and psycho educate the family members. Brief History Mr. H is a 27 years old male studied up to 9th standard working for in FMCG industry at packing department from middle socio economic status from Nelamangala got admitted to NIMHANS for the first time with the chief complaints of increased anger, increased religiosity, decreased sleep, expansive ideas with insidious onset, continuous in progression, and nil significant of precipitating factor. Patient was apparently doing well, patient was working in kadapa, Andrahapradesh for a brief period where he had a fight with some people outside the lodge. Those people assaulted the patient very badly and patient was brought to his house by a security guard. Patient was seen to collecting garbage and used to keep it safely in one place when asked why he is doing so he used to say that he collects it for his own use. After sometime patient is found laughing and talking to self, he used to wish all the people on the road, collecting flowers and stones, put them in one place and start praying. Patient also increased doing pooja of god Manjunatha and started going for temples very frequently. Patient even used to play music in his room with high volume and dancing with the music. Patient started spending more time watching TV, sleep has been decreased, and did not sleep till 2 o cock and used to talk to self saying that people outside are fighting. For these complaints patient got treatment from NIMHANS in 2001. Recently, patient brought with the above said complaints and it has been reported that they were showing to the private psychiatrist in Shivmogga. There were 5 to 6 episodes of illness reported due to that patient find difficulty at job. The present admission patient was brought to get fitness certificate and join the work. The mental status examination revealed moderately kempt, co operative with elevated mood, delusion of reference, delusion of percecution, and absence of judgment and insight. Clinical Diagnosis: Bipolar Affective Disorder Currently Mania with Psychotic Symptoms Family History: Family Composition: Father: 55 year old, illiterate, working as a farmer in his own land. Mother: 48 years old, illiterate homemaker and works in their field with her husband and she takes all the responsibilities at home and monitors all the work. Sister: 31 years old, illiterate, house maker is married to HOPCOMS employee and settled in Bangalore. Brother: 29 year old, unmarried, studied up to PUC, working as a car driver and financially helps the family. Family Interaction Patterns: Interaction between parents: The Interaction between the parents seems to be cordial. The father takes the important decisions and mother accepts it. Mother is told to be a disciplinarian, very active lady who is very interested to do household work. Interaction between the parents and siblings: Father and mother both are more involved in every interaction. Father is very concerned about the needs of the children and make sure that his children get the best of things. At the same time he also motivates his children to work hard. Interaction between the siblings: The patient is very much attached to his brother and his sister. The patient is more close to his sister. The elder brother is also more affectionate towards the patient and helps financially. Family Dynamics: Boundaries: The boundaries between parents and sibling seem to be open and clear. Subsystem: There are no subsystems formed patient and his wife both are staying with his parents in the same roof. Alignments: There was no alliance or coalitions among the family members. Leadership: Father is the functional leader and mother is the nominal leader of the family. This leadership has been agreed by all the family members. Decision making: Decision making is democratic in nature. Parents and all the family members discuss among themselves before taking any decision in any issue. Role structure of functioning: Father plays the instrumental role in the family and mother plays the expressive role. Mother looks after the household work in the family and the father and elder son play the role of bread winner in the family. Communication: Pattern clear and direct the verbal communication mostly present communication between the family members. Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement is form of appreciation and encouragement and negative reinforcements through admonition were present in the family in equal measures. Cohesiveness: There is healthy connectedness in the family. Family rituals: Family members take part in family rituals like eating together, attending functions celebrating festivals etc. Social support: The family has adequate primary, secondary and tertiary support systems. Personal History: Birth & early development: Patient’s birth was a full term, normal delivery with no post natal complications milestones were reportedly normal, developments were appropriate. Behaviour during childhood: No behavioural abnormalities were reported during childhood. There was no report of neurotic traits. School: Patient joined school at the age of 5 years, and studied till the 9th standard due to financial constraints patient could not continue his studies. He is believed to have had friends during his schooling. Occupation: Patient was working as an Auto driver when he was 19 year old. Patient’s uncle brought him to Bangalore and helped to get a job in FMCG factory. Patient joined the work when he was 21 years old and continued the work till illness has worsened. Sexual history: The patient attained sexual knowledge from books and his friends. No high risk behavior found in the patient. Marital hisotry: Patient got married after he became symptomatic. Patient’s parents thought his marriage may reduce his symptoms so they married patient in the year 2005. Alchol and other substances use: Nil Significant Premorbid Personality: Social relationship: The Patient able to sustain relationships both within and outside the family. He took adequate responsibility of his family and was concerned with its well being. Inter personal relationship with the family members and with neighborhoods were appropriate. Mood: The Mood of the Patient was generally euthymic. Attitude to self: Patient was a hardworking and shouldering all the responsibilities of his home. Religious and moral standards: The patient is believed to be religious. He is seemed to behave good moral standards. Leisure activities: The Patient spends his time in watching TV, reading, listening music and going outside with friends. Fantacy life: Patient did not report of any day dreaming. Habits: Patient’s biological habits of sleep, appetite and excretion were normal. Social Analysis and Diagnosis: Mr. H is a 27 year old male, born out of a non-consanguineous marriage studied up to 9th standard from middle socio economic status of Nelamangala presented with past history of mental illness with nil significant family and personal history and primordially well adjusted. Social analysis reveals that the patient was born in a nuclear, flexible and democratic kind of family. The patient was extrovert who likes to be always with friends rather than alone. Patient studied up to 9th standard, later due to financial constraints patient couldn’t continue his studies. After discontinuing his studies patient started helping his father and cultivating their own land. Patient helped his father till he attained 19 years after that patient started running the auto rickshaw which he continued for 3 years. Patient’s uncle who brought the patient to Bangalore and helped to get a job in FMCG factory. Patient joined the factory in year 2000. Patient was transferred always to different places like Chennai, Hyderabad, Gulburga, Kadapa and other places. When patient was staying in Kadapa, he got beaten very badly from number of people. Since then patient has developed abnormal behavior. At work place patient started suspecting his coworkers, misbehaving with females not doing any productive work and talking to self was present. In the meantime patient got married thinking that marriage may reduce patient’s symptoms. After the illness started, patient was absent for work very frequently without informing to his immediate officers. For this, patient was suspended and was asked to come with fitness certificate. Psycho Social Intervention: Individual Level: - To facilitate patient an insight about the illness. - To help patient in adjusting to an activity schedule. - To help patient to control his anger outburst. Family Level: - To psycho-educate the family members about nature of patients illness. - To provide supportive therapy to father for emotional ventilation. Each session with patient was for duration of one hour each on an average, where the session with the father was half an hour on an average.
Strategies: 1. Activity Scheduling, 2. Insight oriented Therapy, 3. Problem solving approach, 4. Anger management techniques, 5. Psychoeducation, Process of Intervention: Intervention with the Patient: The main aim of the activity scheduling was to increase the activity level with engaging self in useful tasks and time management. An activity schedule was prepared by the patient with the help of therapist and was reinforced for the way he follow it. Initially patient tried to follow up the activity schedule but gradually patient stopped following the activity schedule. Educated the patient about his illness, explained him how to differentiate his delusional experience with the external reality. The way of ignoring it by paying less attention to it and differentiate it from the happenings in the outside world. Sometimes he was suspicious that his parents are supportive towards his brother and sister and less towards him. Parents used to get upset due to this kind of behavior. In the sessions these issues were addressed at individual level and family level. The patient gradually started accepting the fact after having intensive sessions on the same aspect. The patient used to get anger quickly with his family members during the sessions with the patient. The anger provoking situations were identified then he was trained to practice various anger management techniques. This was done through practical exercise. The main anger techniques were:-
Intervention with the Father: Psycho Education:
Intervention at Occupation Level: Regarding patients fitness certificate, therapist spoke to the Human Resource Manager of the FMCG Factory and explained about illness, symptoms of the illness, manager assured the therapist that once the patient gets better and avails fitness certificate he will deploy the patient on his job. Outcomes:
Future Plans:
Conclusion: The psychosocial assessment and appropriate psychosocial interventions will definitely help persons with Bipolar Affective Disorder and Psychotic Symptom patient as well as their families. The comprehensive psychosocial intervention has to be planned from mental health professionals to avoid further relapse and for positive result. Hence the psychosocial assessment is very important in getting information about the patient and to plan the intervention. References:
|
Categories
All
Social Work Learning Academy50,000 HR PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS. MHR LEARNING ACADEMYGet it on Google Play store
|
SITE MAP
SiteTRAININGJOB |
HR SERVICESOTHER SERVICESnIRATHANKA CITIZENS CONNECT |
NIRATHANKAPOSHOUR OTHER WEBSITESSubscribe |
MHR LEARNING ACADEMY
50,000 HR AND SOCIAL WORK PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
|
|








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





