|
LABOUR LAW PRACTICE TEST – 03
1. As per the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, the letter of appointment does not apply to fixed-term workers. a) True b) False 2. In case of any sudden increase in the volume of work in the core activity which needs to be accomplished in a specified time, the principal employer is allowed to engage contract labour through a contractor. a) True b) False 3. The two months wage period is allowed in the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020. a) Ture b) False 4. In case of the newly employed contract worker does not have a bank account to disburse wages through bank transfer or electronic mode, he can be paid wages in cash for certain months as per the provisions of the code. a) True b) False LABOUR LAW PRACTICE TEST – 02
1. As per the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, the Contractor is not required to issue a letter of appointment to the contract labour he employs. a) True b) False 2. As per the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, an employer is allowed to issue a letter of appointment in his own format. a) True b) False 3. As per the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, it is mandatory for an employer to issue a letter of appointment to the apprentice engaged under the Apprentices Act, 1961. a) Ture b) False 4. As per the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, it is not mandatory for an employer to issue a letter of appointment to the trainees engaged in line with the certified standing orders of the Company. a) True b) False LABOUR LAW PRACTICE TEST – 01
1. Is the definition of WORKER in the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, the same as the Factories Act, 1948? a) Yes b) No 2. As per the Factories Act, 1948 a CASUAL LABOUR employed to perform the work connected with the manufacturing process is a worker. a) True b) False 3. Is an HR EXECUTIVE A WORKER under the Factories Act, 1948? a) Yes b) No 4. The person, who is employed mainly in a MANAGERIAL OR ADMINISTRATIVE CAPACITY is not a worker under the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020. a) True b) False Q1. What activities are not "core activities of an establishment" under the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020?
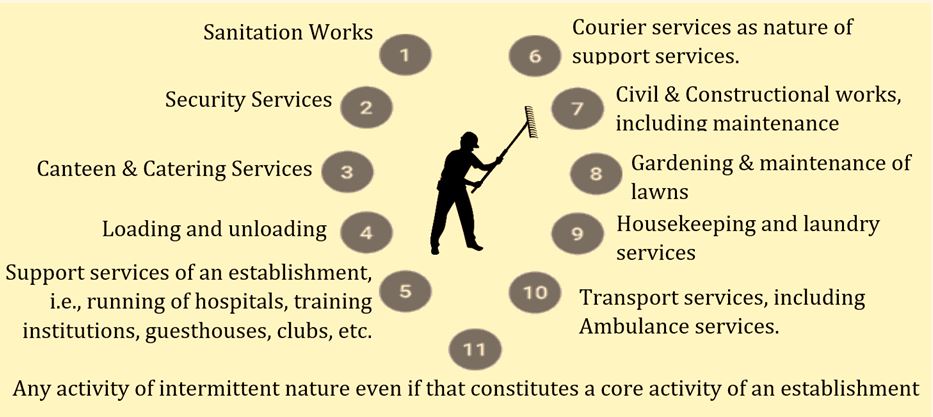
As per section 2 (p) of the code, the following activities are not core activities, if the establishment is not set up for performing such activities: Q1. Which of the existing labour laws the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020, shall repeal?
The Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020 consolidates the following 13 labour laws:
Q1. Is the Principal Employer liable for the payment of wages to the Contract Labour?
Yes. In case, the contractor fails to make payment of wages to its employees, then the principal employer is liable for the payment of wages to the contract labour. As per the Section 21 (4) of the Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act, 1970, in case the contractor fails to make payment of wages or makes short payment to its employees, then the principal employer shall be liable to make the same to concerned contractor’s employees. The principal employer, however, may recover the same from the contractor on the basis of his agreement with the contractor. Q2. Is the Principal Employer liable for the payment of EPF Contribution to the Contract Labour? Yes. In case, if the contractor has not been having/allotted independent Provident Fund Contribution Code Number, in such case the contributions in respect of contractor’s employees shall have to be paid at the first instance by the principal employer. And, later recover the same from the contractor. In case if the contractors is having an independent code number under EPF Act, 1952, in such case the principal employer is not liable to pay the EPF contribution in respect of employees of contractor. |
Categories
All
HR Learning and Skill Building AcademyMHR LEARNING ACADEMYGet it on Google Play store
|
SITE MAP
SiteTRAININGJOB |
HR SERVICESOTHER SERVICESnIRATHANKA CITIZENS CONNECT |
NIRATHANKAPOSHOUR OTHER WEBSITESSubscribe |
MHR LEARNING ACADEMY
50,000 HR AND SOCIAL WORK PROFESSIONALS ARE CONNECTED THROUGH OUR NIRATHANKA HR GROUPS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
YOU CAN ALSO JOIN AND PARTICIPATE IN OUR GROUP DISCUSSIONS.
|
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





